Smoothing
This page provides a general overview of smoothing methods.
Lowess Method
Smoothing is done using the lowess command in Stata, on individual level estimates for key variables. The syntax in smoothing labor income estimates for Taiwan:
lowess yl age, bwidth(0.1) gen(syvar) nograph
Where yl is the key variable to be smoothed; bwidth(*) specifies the bandwith and gen(*) is used to save smoothed values. (Graphs are supressed using the nograph option.) Key variables include consumption (health and other, education is not being smoothed at this time), labor income, housing, and taxes. Lowess is used to carry out a locally weighted regression of the key variable on age, making use of the option to save the smoothed variable. Smoothed variables are then used to produce the smoothed age profiles.
The default bandwidth in Stata is 0.8; for Taiwan estimates, a bandwidth of 0.1 was used. The optimal bandwidth is dependent on the variable and dataset, and is determined through examination of smoothed profiles plotted against unsmoothed ones. A larger bandwith increases the smoothing, eliminating more of the variation inherent in the unsmoothed variables. Once smoothed variables are obtained, a plot of the smoothed and unsmoothed age profiles should be done to ensure that smoothing was carried out properly. Age profiles of labor income for Taiwan (1998), using varying bandwidths, are provided below for illustration:
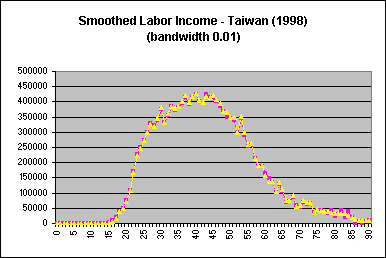
| Too narrow a bandwidth results in smoothed estimates that are still noisy. |
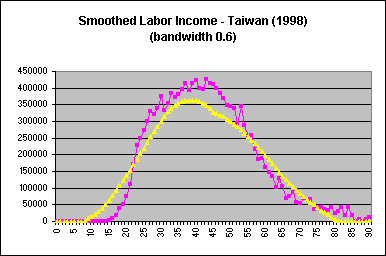
| A bandwidth that is too wide does not provide an accurate representation of the unsmoothed data. |
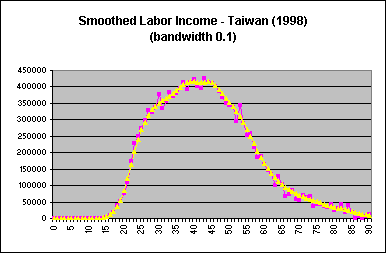
| The proper bandwidth smoothes out extreme values and excess noise, but the general shape of the age profile remains. |
Smoothed estimates of key variables are then used in futher calculations, and no further smoothing is done.
Warnings and Caveats
In some instances Stata will produce smoothed values that consistently larger (or smaller) than unsmoothed values. One explanation, as in the case of Thailand below, is the effect of weighting. The lowess command does not allow the incorporation of weights when smoothing. When the use of weights significantly affects the shape of the age profile the following may occur:
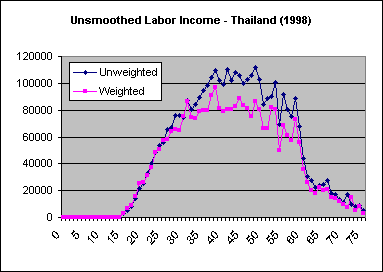
| In the case of Thailand, there are significant differences in the shapes of weighted and unweighted profiles. |
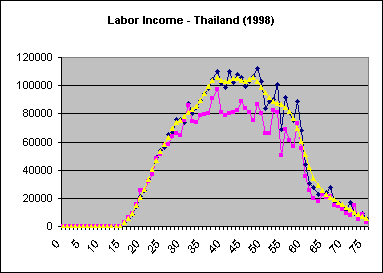
| Smoothing results in estimates that are systematically greater than those of the unsmoothed weighted profile, but are consistent with the unweighted profile. |
One possible solution is pre-weighting data before smoothing is applied. However, as lowess is computationally intensive, smoothing weighted data is extremely time consuming.
Using Lowess with Sample Weights
Friedman's SuperSmoother (work in progress)
Comments about smoothing:
